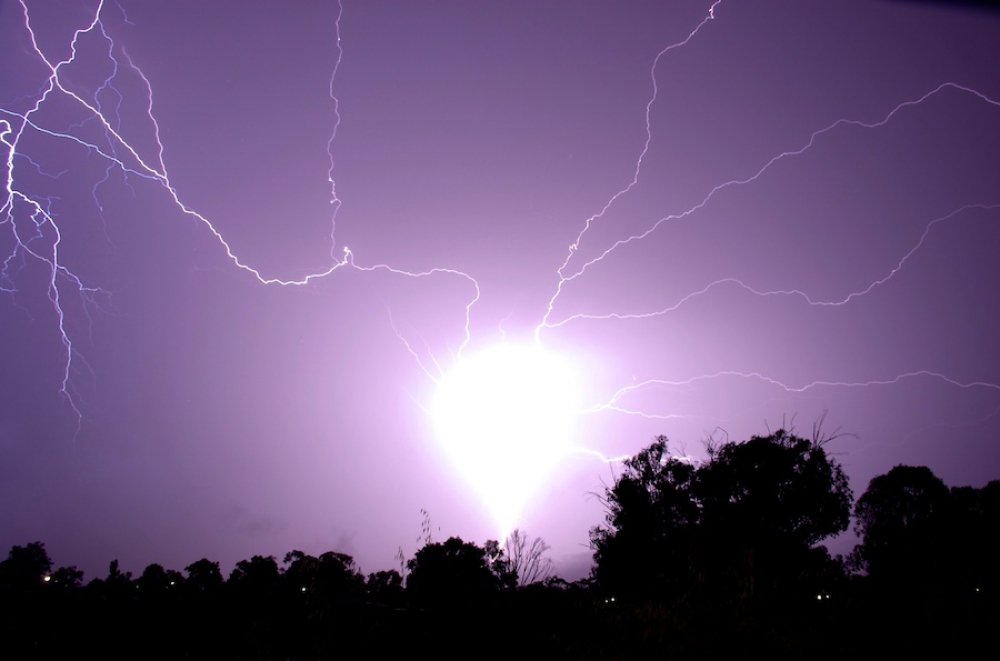
Where does ball lightning come from and what is it? Scientists have been asking themselves this question for many decades in a row, and so far there is no clear answer. A stable plasma ball resulting from a powerful high-frequency discharge. Another hypothesis is antimatter micrometeorites.
In total, there are more than 400 unproven hypotheses.
...A barrier with a spherical surface can arise between matter and antimatter. Powerful gamma radiation will inflate this ball from the inside, and prevent the penetration of matter to the incoming antimatter, and then we will see a glowing pulsating ball that will hover above the Earth. This point of view seems to have been confirmed. Two English scientists methodically examined the sky using gamma radiation detectors. And they recorded four times an anomalously high level of gamma radiation in the expected energy region.
The first documented case of ball lightning took place in 1638 in England, in one of the churches in Devon County. As a result of the outrages of the huge fireball, 4 people were killed and about 60 were injured. Subsequently, new reports of similar phenomena periodically appeared, but there were few of them, since eyewitnesses considered ball lightning an illusion or an optical illusion.
The first generalization of cases of a unique natural phenomenon was made by the Frenchman F. Arago in the middle of the 19th century; his statistics collected about 30 pieces of evidence. The increasing number of such meetings made it possible to obtain, based on the descriptions of eyewitnesses, some characteristics inherent in the heavenly guest. Ball lightning is an electrical phenomenon, a fireball moving in the air in an unpredictable direction, glowing, but not emitting heat. This is where the general properties end and the specifics characteristic of each case begin. This is explained by the fact that the nature of ball lightning is not fully understood, since until now it has not been possible to study this phenomenon in laboratory conditions or to recreate a model for study. In some cases, the diameter of the fireball was several centimeters, sometimes reaching half a meter.
Ball lightning has been the object of study by many scientists for several hundred years, including N. Tesla, G. I. Babat, P. L. Kapitsa, B. Smirnov, I. P. Stakhanov and others. Scientists have put forward different theories of the occurrence of ball lightning, of which there are over 200. According to one version, the electromagnetic wave formed between the earth and the clouds at a certain moment reaches a critical amplitude and forms a spherical gas discharge. Another version is that ball lightning consists of high-density plasma and contains its own microwave radiation field. Some scientists believe that the fireball phenomenon is the result of clouds focusing cosmic rays. Most cases of this phenomenon were recorded before and during a thunderstorm, so the most relevant hypothesis is the emergence of an energetically favorable environment for the appearance of various plasma formations, one of which is lightning. Experts agree that when meeting a heavenly guest, you need to adhere to certain rules of behavior. The main thing is not to make sudden movements, not to run away, and try to minimize air vibrations.
Their “behavior” is unpredictable, their trajectory and flight speed defy any explanation. They, as if endowed with intelligence, can bend around the obstacles facing them - trees, buildings and structures, or they can “crash” into them. After this collision, fires may occur.
Ball lightning often flies into people's homes. Through open windows and doors, chimneys, pipes. But sometimes even through a closed window! There is a lot of evidence of how the CMM melted window glass, leaving behind a perfectly smooth round hole.
According to eyewitnesses, fireballs appeared from the socket! They “live” from one to 12 minutes. They can simply disappear instantly, leaving no traces behind, but they can also explode. The latter is especially dangerous. These explosions can result in fatal burns. It was also noticed that after the explosion, a rather persistent, very unpleasant smell of sulfur remains in the air.
Ball lightning comes in different colors - from white to black, from yellow to blue. When moving, they often hum, like high-voltage power lines hum.
It remains a big mystery what influences the trajectory of its movement. This is definitely not the wind, since she can move against it. This is not a difference in atmospheric phenomenon. These are not people or other living organisms, since sometimes it can peacefully fly around them, and sometimes it “crashes” into them, which leads to death.
Ball lightning is evidence of our very poor knowledge of such a seemingly ordinary and already studied phenomenon as electricity. None of the previously put forward hypotheses has yet explained all of its quirks. What is proposed in this article may not even be a hypothesis, but only an attempt to describe the phenomenon in a physical way, without resorting to exotic things like antimatter. The first and main assumption: ball lightning is a discharge of ordinary lightning that has not reached the Earth. More precisely: ball and linear lightning are one process, but in two different modes - fast and slow.
When switching from a slow mode to a fast one, the process becomes explosive - ball lightning turns into linear lightning. The reverse transition of linear lightning to ball lightning is also possible; In some mysterious, or perhaps random way, this transition was accomplished by the talented physicist Richman, a contemporary and friend of Lomonosov. He paid for his luck with his life: the ball lightning he received killed its creator.
Ball lightning and the invisible atmospheric charge path connecting it to the cloud are in a special “elma” state. Elma, unlike plasma - low-temperature electrified air - is stable, cools and spreads very slowly. This is explained by the properties of the boundary layer between the Elma and ordinary air. Here the charges exist in the form of negative ions, bulky and inactive. Calculations show that the elms spread out in as much as 6.5 minutes, and they are replenished regularly every thirtieth of a second. It is through this time interval that an electromagnetic pulse passes in the discharge path, replenishing Kolobok with energy.
Therefore, the duration of the existence of ball lightning is in principle unlimited. The process should stop only when the charge of the cloud is exhausted, more precisely, the “effective charge” that the cloud is able to transfer to the route. This is exactly how one can explain the fantastic energy and relative stability of ball lightning: it exists due to the influx of energy from the outside. Thus, the neutrino phantoms in Lem’s science fiction novel “Solaris,” possessing the materiality of ordinary people and incredible strength, could only exist with the supply of colossal energy from the living Ocean.
The electric field in ball lightning is close in magnitude to the level of breakdown in a dielectric, whose name is air. In such a field, the optical levels of atoms are excited, which is why ball lightning glows. In theory, weak, non-luminous, and therefore invisible ball lightning should be more frequent.
The process in the atmosphere develops in the mode of ball or linear lightning, depending on the specific conditions in the path. There is nothing incredible or rare in this duality. Let's remember ordinary combustion. It is possible in the mode of slow flame propagation, which does not exclude the mode of a rapidly moving detonation wave.
...Lightning comes down from the sky. It is not yet clear what it should be, spherical or regular. It greedily sucks the charge from the cloud, and the field in the path decreases accordingly. If, before hitting the Earth, the field in the path falls below a critical value, the process will switch to the ball lightning mode, the path will become invisible, and we will notice that ball lightning is descending to the Earth.
The external field in this case is much smaller than the own field of ball lightning and does not affect its movement. This is why bright lightning moves chaotically. Between flashes, ball lightning glows weaker and its charge is small. The movement is now directed by the external field and is therefore linear. Ball lightning can be carried by wind. And it's clear why. After all, the negative ions that it consists of are the same air molecules, only with electrons stuck to them.
The rebound of ball lightning from the near-Earth “trampoline” layer of air is simply explained. When ball lightning approaches the Earth, it induces a charge in the soil, begins to release a lot of energy, heats up, expands and quickly rises under the influence of the Archimedean force.
Ball lightning plus the surface of the Earth forms an electrical capacitor. It is known that a capacitor and a dielectric attract each other. Therefore, ball lightning tends to locate itself above dielectric bodies, which means it prefers to be above wooden walkways or above a barrel of water. The long-wave radio emission associated with ball lightning is created by the entire path of the ball lightning.
The hiss of ball lightning is caused by bursts of electromagnetic activity. These flashes occur at a frequency of about 30 hertz. The hearing threshold of the human ear is 16 hertz.
Ball lightning is surrounded by its own electromagnetic field. Flying past an electric light bulb, it can inductively heat and burn out its filament. Once in the wiring of a lighting, radio broadcasting or telephone network, it closes its entire route to this network. Therefore, during a thunderstorm, it is advisable to keep the networks grounded, say, through discharge gaps.
Ball lightning, “spread out” over a barrel of water, together with the charges induced in the ground, forms a capacitor with a dielectric. Ordinary water is not an ideal dielectric; it has significant electrical conductivity. Current begins to flow inside such a capacitor. Water is heated by Joule heat. The “barrel experiment” is well known, when ball lightning heated about 18 liters of water to a boil. According to theoretical estimates, the average power of ball lightning when it floats freely in the air is approximately 3 kilowatts.
In exceptional cases, for example in artificial conditions, an electrical breakdown may occur inside ball lightning. And then plasma appears in it! In this case, a lot of energy is released, artificial ball lightning can shine brighter than the Sun. But usually the power of ball lightning is relatively small - it is in the elma state. Apparently, the transition of artificial ball lightning from the elma state to the plasma state is possible in principle.
Knowing the nature of the electric Kolobok, you can make it work. Artificial ball lightning can greatly exceed the power of natural lightning. By drawing an ionized trace along a given trajectory in the atmosphere with a focused laser beam, we will be able to direct ball lightning where we need it. Let's now change the supply voltage and transfer the ball lightning to linear mode. Giant sparks will obediently rush along the trajectory we have chosen, crushing rocks and felling trees.
There is a thunderstorm over the airfield. The airport terminal is paralyzed: landing and takeoff of aircraft is prohibited... But the start button is pressed on the control panel of the lightning dissipation system. A fiery arrow shot up into the clouds from a tower near the airfield. This artificial controlled ball lightning that rose above the tower switched to linear lightning mode and, rushing into a thundercloud, entered it. The lightning path connected the cloud to the Earth, and the electrical charge of the cloud was discharged to the Earth. The process can be repeated several times. There will be no more thunderstorms, the clouds have cleared. Planes can land and take off again.
In the Arctic, it will be possible to light an artificial sun. A three-hundred-meter charge path of artificial ball lightning rises up from a two-hundred-meter tower. Ball lightning switches on to plasma mode and shines brightly from a height of half a kilometer above the city.
For good illumination in a circle with a radius of 5 kilometers, ball lightning is sufficient, emitting a power of several hundred megawatts. In artificial plasma mode, such power is a solvable problem.
The Electric Gingerbread Man, who for so many years has avoided making close acquaintance with scientists, will not leave: sooner or later he will be tamed, and he will learn to benefit people. B. Kozlov.
1. What ball lightning is is still not known for certain. Physicists have not yet learned how to reproduce real ball lightning in laboratory conditions. Of course, they get something, but scientists don’t know how similar this “something” is to real ball lightning.
2. When there is no experimental data, scientists turn to statistics - to observations, eyewitness accounts, rare photographs. In fact, rare: if there are at least one hundred thousand photographs of ordinary lightning in the world, then there are much fewer photographs of ball lightning - only six to eight dozen.
3. The color of ball lightning can be different: red, dazzling white, blue, and even black. Witnesses saw ball lightning in all shades of green and orange.
4. Judging by the name, all lightning should have the shape of a ball, but no, both pear-shaped and egg-shaped ones were observed. Particularly lucky observers saw lightning in the form of a cone, ring, cylinder, and even in the form of a jellyfish. Someone saw a white tail behind the lightning.
5. According to the observations of scientists and eyewitness accounts, ball lightning can appear in a house through a window, door, stove, or even just appear out of nowhere. It can also be blown out of an electrical outlet. In the open air, ball lightning can appear from a tree and a pole, descend from the clouds, or be born from ordinary lightning.
6. Usually ball lightning is small - fifteen centimeters in diameter or the size of a football, but there are also five-meter giants. Ball lightning does not live long - usually no more than half an hour, moves horizontally, sometimes rotating, at a speed of several meters per second, sometimes hangs motionless in the air.
7. Ball lightning shines like a hundred-watt light bulb, sometimes crackles or squeaks and usually causes radio interference. Sometimes it smells like nitrogen oxide or the hellish smell of sulfur. If you're lucky, it will quietly dissolve into thin air, but more often it explodes, destroying and melting objects and evaporating water.
8. “...A red-cherry spot is visible on the forehead, and a thunderous electric force came out of it from the legs into the boards. The legs and toes are blue, the shoe is torn, not burned...” This is how the great Russian scientist Mikhail Vasilyevich Lomonosov described the death of his colleague and friend Richman. He was still worried “that this case would not be interpreted against the advancement of science,” and he was right in his fears: electricity research was temporarily banned in Russia.
9. In 2010, Austrian scientists Josef Peer and Alexander Kendl from the University of Innsbruck suggested that evidence of ball lightning could be interpreted as a manifestation of phosphenes, that is, visual sensations without exposure to light on the eye. Their calculations show that the magnetic fields of certain repeated lightning strikes induce electric fields in neurons in the visual cortex. Thus, ball lightning is a hallucination.
The theory was published in the scientific journal Physics Letters A. Now supporters of the existence of ball lightning must register ball lightning with scientific equipment, and thus refute the theory of Austrian scientists.
10. In 1761, ball lightning entered the church of the Vienna Academic College, tore off the gilding from the cornice of the altar column and deposited it on the silver crypt. People have a much harder time: at best, ball lightning will burn you. But it can also kill - like Georg Richmann. Here's a hallucination for you!
Ball lightning - a beautiful myth or? Thousands of people around the world claim to have personally seen it - a glowing, roughly spherical ball of light. As a rule, this phenomenon is observed during a thunderstorm, but the details of the observations vary greatly. The fireballs range in size from a few centimeters to a meter or more. They can be red, blue, yellow, white or even green. Their lifetime ranges from several seconds to several minutes. They disappear without a trace or explode, causing destruction and harm. What is ball lightning and what to do if you encounter it?
Characteristics of a natural phenomenon
They can wander above the ground or descend from the sky, hang motionless or fly at impressive speed, radiate heat or appear completely cold. There is evidence of ball lightning appearing on flying airplanes and traveling over the heads of stunned passengers. Some eyewitnesses even claim that the shining balls move and behave like living beings. Sometimes they stay at a distance, sometimes they circle around as if with curiosity, and often they “attack.”

Contact with the mysterious ball can result in burns or even death. If a thunderstorm is raging outside the window, can ball lightning pass through the glass? Yes, and even through the wall, as numerous witnesses to such incidents say. Therefore, it is not surprising that people ask a logical question: if there really is ball lightning in nature, how to behave in the presence of it and protect yourself?
Famous philosophers and scientists such as Lucius Seneca, Niels Bohr and Peter Kapitsa carefully studied the phenomenon of ball lightning. Modern physicists, who have long doubted the reliability of this amazing phenomenon, are now trying to formulate a plausible explanation for its existence, which is no longer in doubt. But it has not yet been possible to get clear answers to the accumulated questions.
What is ball lightning and what should you do when encountering it? Why does she move along unpredictable trajectories and “behave” so strangely? What energy source supports it? In what cases does it pose a threat to people, and in what cases is it harmless?

What to do if ball lightning strikes?
Many scientific and amateur versions have been put forward about the physics and origin of the strange phenomenon, but so far none of them have been confirmed. It has not yet been possible to obtain ball lightning in the laboratory either. Today we can only guess what this mysterious luminous sphere is.
All that remains for people is to follow all recommendations regarding a possible meeting with the phenomenon. They boil down to the utmost caution:
To reduce this dangerous phenomenon, you need to keep the windows and doors in your house closed during a thunderstorm. Can ball lightning pass through window glass? Unfortunately yes. However, it is believed that it mainly moves in air currents and “loves” drafts, so you should not create them.
Questions about the existence of ball lightning - a glowing electric ball hovering above the earth - have bothered scientists for many centuries, creating a huge layer of myths and legends around it. This mystical natural phenomenon, which can also be called “earth lightning,” usually appears during a thunderstorm in the form of a sphere drifting above the ground - the colors of these objects vary from orange to yellow. The phenomenon usually does not last long - only a couple of seconds, but is accompanied by hissing and a pungent odor.
Lightning, as such, is an electrical discharge caused by a positive and negative imbalance within the clouds themselves or between thunderclouds and the ground. A lightning flash can heat the air around it to temperatures five times higher than the sun. High temperatures cause the surrounding air to rapidly expand and vibrate, hence thunder.
What is ball lightning?
Ball lightning is a luminous spherical clot of electric current. Even if it exists, and some scientists doubt it, it is very rare. However, many amazing stories are known about the tricks of ball lightning.
What does ball lightning look like?

Descriptions of ball lightning differ greatly from each other, so it is not possible to accurately answer the question posed. Thus, some eyewitnesses described them as moving up and down, others - to the side, others - along an unpredictable trajectory, others - were in a static position, and others - against the wind. There were also claims that ball lightning could be repelled from people, cars or buildings without any impact; others claim that this phenomenon, on the contrary, is attracted by surrounding objects.
Some eyewitnesses claim that ball lightning is capable of passing through solid objects - metals, trees without any effect; others say that upon contact with the “fireball,” substances explode, melt, or are otherwise destroyed. There was evidence of lightning occurring near power lines, at different heights, in thunderstorms and in calm weather.
Eyewitnesses gave the phenomenon many different appearances - transparent, translucent, multi-colored, evenly illuminated, emitting flames, threads or sparks; and its shapes vary no less - spheres, ovals, drops, rods or disks. Some often confuse ball lightning with St. Elmo's Fire, but you need to understand that these are two different natural phenomena.
Related materials:
Why is it raining?

The orbs were reported to disappear in a variety of ways - evaporating, abruptly disappearing, gradually dissipating, being absorbed by nearby objects, crackling, loudly exploding, or even causing damage to everything around them. The danger to people also differs greatly from witness to witness - some talk about complete harmlessness, others frighten with mortal danger.
In 1972, an attempt was made to analyze all available information about ball lightning and create the most accurate image of this mystery of nature. It turned out that the fire sphere has the following properties:
- appears almost simultaneously with a lightning discharge;
- usually has a spherical or pear-shaped shape;
- diameter varies from 1 to 100 cm;
- the brightness is about the same as that of a regular table lamp;
- there is a wide range of possible colors, the most common being red, orange and yellow;
- the duration of “life” is from 1 second to a whole minute. The brightness is maintained throughout the entire phenomenon;
- usually moves, but mostly horizontally at a speed of several meters per second.
- sometimes they can move vertically or simply stand still;
- can make rotational movements;
- some witnesses reported feeling hot when close to lightning;
- strive for metals;
- can appear in buildings by passing through doors and windows;
- some appeared in metal planes without causing any damage;
- disappearance can occur either with an explosion or in the form of silent evaporation;
Odors often reported are ozone, sulfur or nitrogen oxide.
Types of ball lightning
Based on eyewitness accounts, two types of ball lightning are distinguished. The first is a red lightning bolt descending from a cloud. When such a heavenly gift touches any object on earth, for example a tree, it explodes.
Interesting: Ball lightning can be the size of a football and can hiss and buzz threateningly.
Another type of ball lightning travels along the earth's surface for a long time and glows with a bright white light. The ball is attracted to good conductors of electricity and can touch anything - the ground, a power line or a person.

Eyewitness accounts
Observations of ball lightning go far into the wilds of human history. Many eyewitness accounts have been recorded of such a rare and amazing natural phenomenon. But even despite the large number of eyewitness testimonies, until 2010, the theory of the existence of ball lightning was a big question.
Related materials:
Why are the stars brighter in winter?
And while the scientific world is in ignorance and controversy, offering as many as 400 different theories, you can draw your own conclusion about the reality of ball lightning by reading the history of recorded eyewitness accounts of this mystery of nature.
Thunderstorm at Widecombe-in-the-Moor
One of the earliest accounts tells of the “Great Storm” that occurred at Widecombe-in-the-Moor Church in Devon, England, on October 21, 1638. During a strong storm, a huge luminous ball flew into the church, almost completely destroying it. Stone elements and huge wooden beams were thrown many meters in different directions. Eyewitnesses stated that the lightning destroyed everything in its path - benches and glass - it filled the entire church with a sulfurous smell and dark thick smoke.

The victims said that the mysterious ball at some point split into two parts - one of them came out of the window, breaking it, and the other evaporated in the church itself.
Eyewitnesses - due to the smell of sulfur and the destructive power of the phenomenon - agreed that it was the devil himself, who brought down God's wrath on people. It was believed that two parishioners were to blame for everything, who decided to play cards during the sermon.
Ebenezer Cobham Brewer
Ebenezer Cobham Brewer, an English writer, in 1864, in his book “A Guide to the Scientific Knowledge of Things,” talks about ball lightning. There he describes the phenomenon as slow-moving balls of fire and gas that can fall to the ground or move quickly across it during a thunderstorm. The writer talked about how the balls could explode “like a cannon.”

Wilfried de Fonvielle
In his book Thunder and Lightning, French writer Wilfried de Fonvielle claims that more than 150 reports of ball lightning have been recorded.

These are probably the most famous cases in history, but there were many others.
On April 30, 1877, ball lightning flew into the Golden Temple in Amritsar, India, and exited through a side door. Several people witnessed this phenomenon and the incident is recorded on the front wall of Darshani Deodhi;
Pilots in World War II described an unusual phenomenon, for which ball lightning was proposed as an explanation. They saw small balls of light moving in strange trajectories, which became known as foo fighters.
In 2005, there was an incident in the skies over Guernsey when a plane was struck by lightning. Witnesses to this event stated that they saw ball lightning.
Related materials:
Why are lightning bolts different colors?
On December 15, 2014, on flight BE-6780 in the UK, passengers observed ball lightning in the front cabin shortly before lightning struck the aircraft.
How is ball lightning formed?
Visual hallucination
In 2010, scientists from the Austrian University of Innsbruck published their hypothesis, which for the first time fell under Popper's criteria (that is, it is the first hypothesis that can be considered scientific). Experts believed that the phenomenon of ball lightning is not a natural anomaly, but only a phosphene (that is, a visual hallucination that occurs without direct exposure to light on the eye receptors, causing the observed images of luminous points and figures that appear in the dark).
Peer and Kendel theorize that changing environmental conditions caused by lightning strikes affect people's optic nerves in such a way that they think they see ball lightning. A similar effect can be caused even at a distance of 100 meters from the immediate point of lightning strike.
For two years, this theory was considered the main one, and it seemed to the scientific world that the issue had been resolved, but in 2012, something happened in the Tibetan plateau region that returned ball lightning to the agenda. Chinese meteorologists who installed spectrometers to observe ordinary lightning, were able to record the glow of ball lightning. It lasted exactly 1.64 seconds, and specialists were able to record its detailed spectra. They are very different from normal lightning, which contains lines of ionized nitrogen, whereas ball lightning had iron, silicon and calcium contained in the soil.
Thus, we can conclude that the hypothesis of the Austrian scientists is not exhaustive. But There is still not a single irrefutable theory about why such an anomaly occurs. AND many experts generally doubt its existence.
Chemical reaction
Chinese meteorologists from Lanzhou, who recorded ball lightning in 2012, published their hypothesis of the occurrence of ball lightning. So they suggested that the anomaly arises due to certain chemical reactions between oxygen and elements that evaporate from the soil when struck by lightning. This ionized air, or plasma, can also cause another effect called St. Elmo's Fire (which is a stationary glow that often appears at the ends of ship masts. It is sometimes confused with ball lightning).
But this was not the only theory that was published in 2012. At the same time, another assumption was made, according to which glass could become a source of ball lightning. Thus, experts suggest that ions from the atmosphere can accumulate on the surface of the glass, and if their concentration is sufficient, a discharge is generated, which becomes ball lightning. Four years after these two studies, an article appeared where it was reported that microwave radiation arising from a lightning strike could be “encapsulated” in a certain ball of plasma - this is ball lightning.
Microwave rays
But scientists tried not only to analyze evidence that came from the past, but also tried to recreate this mysterious phenomenon in laboratory conditions. So Israeli specialists from the University of Tel Aviv were able to cause their own version of ball lightning using microwave rays. In a very recent experiment conducted in 2018, quantum physicists decided to create ball lightning using a synthetically coupled magnetic field.
But these are not all theories of the appearance of ball lightning, but only the most recent of them. Scientists continue to puzzle over such an elusive phenomenon, which is not a fact that even exists.
Laboratory experiments
Scientists have long tried to recreate ball lightning in the laboratory. Although some experiments have produced effects that are visually similar to evidence of natural ball lightning, it has not yet been confirmed whether there is any connection between them.
According to reports, Nikola Tesla could artificially create small luminous balls with a diameter of 30-40 mm, and also conducted some demonstrations of his skills. But this was just a hobby for the great scientist, so he did not leave any notes or explanations. He was more interested in higher voltages and powers, as well as remote energy transfer, so the balls he made were simply an expression of curiosity.
The International Committee on Ball Lightning (ICBL) regularly held symposia on this topic. The group uses the general name "Unconventional Plasma". The last ICBL symposium was tentatively scheduled for July 2012 in San Marcos, Texas, but was canceled due to a lack of abstract submissions.